this is my refference when I create Load balacing Speedy + ISP .
I will write what excact my experience letter
Regards
Suwidi
Load Balancing over Multiple Gateways
From MikroTik Wiki
The typical situation where you got one router and want to connect to two ISPs:
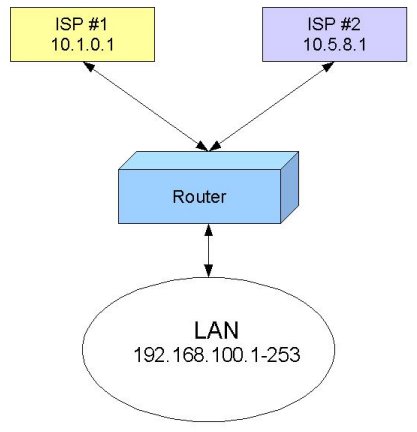
Of course, you want to do load balancing! There are several ways how to do it. Depending on the particular situation, you may find one best suited for you.
[ edit] Policy Routing based on Client IP Address
If you have a number of hosts, you may group them by IP addresses. Then, depending on the source IP address, send the traffic out through Gateway #1 or #2. This is not really the best approach, giving you perfect load balancing, but it's easy to implement, and gives you some control too.
Let us assume we use for our workstations IP addresses from network 192.168.100.0/24. The IP addresses are assigned as follows:
- 192.168.100.1-127 are used for Group A workstations
- 192.168.100.128-253 are used for Group B workstations
- 192.168.100.254 is used for the router.
All workstations have IP configuration with the IP address from the relevant group, they all have network mask 255.255.255.0, and 192.168.100.254 is the default gateway for them. We will talk about DNS servers later.
Now, when we have workstations divided into groups, we can refer to them using subnet addressing:
If you do not understand this, take the TCP/IP Basics course,
or, look for some resources about subnetting on the Internet!
We need to add two IP Firewall Mangle rules to mark the packets originated from Group A or Group B workstations.
For Group A, specify
- Chain prerouting and Src. Address 192.168.100.0/25
- Action mark routing and New Routing Mark GroupA.
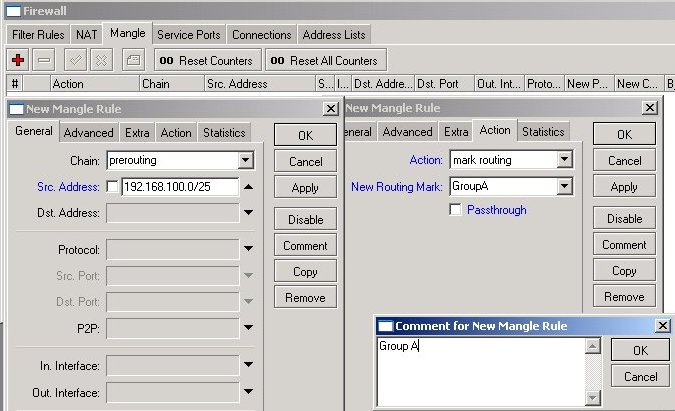
It is a good practice to add a comment as well. Your mangle rules might be interesting for someone else and for yourself as well after some time.
For Group B, specify
- Chain prerouting and Src. Address 192.168.100.128/25
- Action mark routing and New Routing Mark GroupB
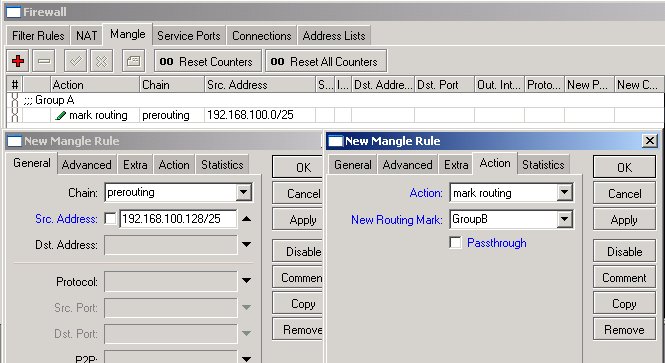
All IP traffic coming from workstations is marked with the routing marks GroupA or GroupB. We can use these marks in the routing table.
Next, we should specify two default routes (destination 0.0.0.0/0) with appropriate routing marks and gateways:
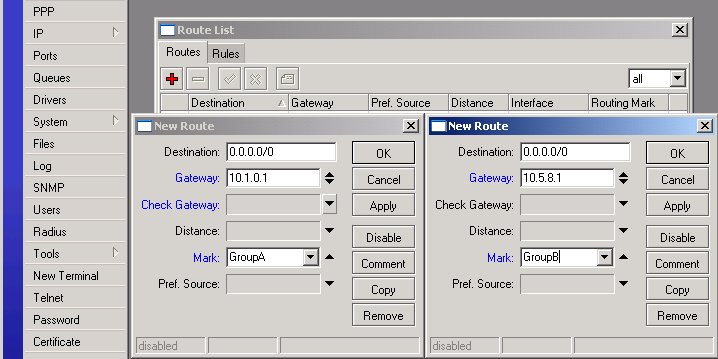
This thing is not going to work, unless you do masquerading for your LAN! The simplest way to do it is by adding one NAT rule for Src. Address 192.168.100.0/24 and Action masquerade:
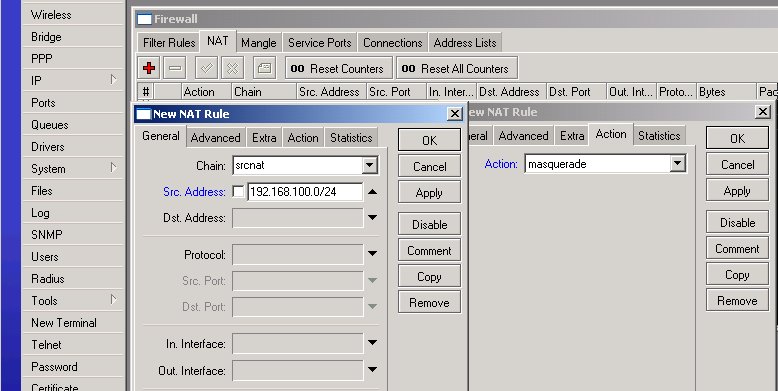
Test the setup by tracing the route to some IP address on the Internet!
From a workstation of Group A, it should go like this:
C:\>tracert -d 8.8.8.8
Tracing route to 8.8.8.8 over a maximum of 30 hops
1 2 ms 2 ms 2 ms 192.168.100.254
2 10 ms 4 ms 3 ms 10.1.0.1
...
From a workstation of Group B, it should go like this:
C:\>tracert -d 8.8.8.8
Tracing route to 8.8.8.8 over a maximum of 30 hops
1 2 ms 2 ms 2 ms 192.168.100.254
2 10 ms 4 ms 3 ms 10.5.8.1
...
You can specify the DNS server for workstations quite freely, just make it can be reached (test it by tracing the route to DNS server's IP address)!
Routes, Equal Cost Multipath Routing, Policy Routing
| Document revision: | 2.3 (July 20, 2007, 13:21 GMT) |
| Applies to: | V2.9 |
General Information
Summary
The following manual surveys the IP routes management, equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) routing technique, and policy-based routing.
Specifications
Packages required:
system License required:
Level1 Submenu level:
/ip route Standards and Technologies:
IP (RFC 791) Hardware usage:
Not significant Related Documents
Description
MikroTik RouterOS has following types of routes:
- dynamic routes - automatically created routes for networks, which are directly accessed through an interface. They appear automatically, when adding a new IP address. Dynamic routes are also added by routing protocols.
- static routes - user-defined routes that specify the router which can forward traffic to the specified destination network. They are useful for specifying the default gateway
This routing mechanism enables packet routing along multiple paths with equal cost and ensures load balancing. With ECMP routing, you can use more than one gateway for one destination network (Note! This approach does not provide failover). With ECMP, a router potentially has several available next hops towards a given destination. A new gateway is chosen for each new source/destination IP pair. It means that, for example, one FTP connection will use only one link, but new connection to a different server will use another link. ECMP routing has another good feature - single connection packets do not get reordered and therefore do not kill TCP performance.
The ECMP routes can be created by routing protocols (RIP or OSPF), or by adding a static route with multiple gateways, separated by a comma (e.g., /ip route add gateway=192.168.0.1,192.168.1.1). The routing protocols may create multipath dynamic routes with equal cost automatically, if the cost of the interfaces is adjusted properly. For more information on using routing protocols, please read the corresponding Manual.
Policy-Based Routing It is a routing approach where the next hop (gateway) for a packet is chosen, based on a policy, which is configured by the network administrator. In RouterOS the procedure the follwing:
- mark the desired packets, with a routing-mark
- choose a gateway for the marked packets
Note! In routing process, the router decides which route it will use to send out the packet. Afterwards, when the packet is masqueraded, its source address is taken from the prefsrc field.
Routes
Submenu level:
/ip route Description
In this submenu you can configure Static, Equal Cost Multi-Path and Policy-Based Routing and see the routes.
Property Description
as-path (
text) - manual value of BGP's as-path for outgoing route
atomic-aggregate (yes | no) - BGP attribute. An indication to receiver that it cannot "deaggregate" the prefix
check-gateway (arp | ping; default:
ping) - which protocol to use for gateway reachability
distance (
integer: 0..255) - administrative distance of the route. When forwarding a packet, the router will use the route with the lowest administrative distance and reachable gateway
dst-address (
IP address/
netmask; default:
0.0.0.0/0) - destination address and network mask, where netmask is number of bits which indicate network number. Used in static routing to specify the destination which can be reached, using a gateway
gateway (
IP address) - gateway host, that can be reached directly through some of the interfaces. You can specify multiple gateways separated by a comma "," for ECMP routes
local-pref (
integer) - local preference value for a route
med (
integer) - a BGP attribute, which provides a mechanism for BGP speakers to convey to an adjacent AS the optimal entry point into the local AS
origin (incomplete | igp | egp) - the origin of the route prefix
prefsrc (
IP address) - source IP address of packets, leaving router via this route
0.0.0.0 - prefsrc is determined automatically
prepend (
integer: 0..16) - number which indicates how many times to prepend AS_NAME to AS_PATH
routing-mark (
name) - a mark for packets, defined under
/ip firewall mangle. Only those packets which have the according routing-mark, will be routed, using this gateway. With this parameter we provide policy based routing
scope (
integer: 0..255) - a value which is used to recursively lookup the nexthop addresses. Nexthop is looked up only through routes that have scope <= target-scope of the nexthop
target-scope (
integer: 0..255) - a value which is used to recursively lookup the next-hop addresses. Each nexthop address selects smallest value of target-scope from all routes that use this nexthop address. Nexthop is looked up only through routes that have scope <= target-scope of the nexthop
Notes
You can specify more than one or two gateways in the route. Moreover, you can repeat some routes in the list several times to do a kind of cost setting for gateways.
Example
To add two static routes to networks 10.1.12.0/24 and 0.0.0.0/0 (the default destination address) on a router with two interfaces and two IP addresses:
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> add dst-address=10.1.12.0/24 gateway=192.168.0.253
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> add gateway= 10.5.8.1
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> print
Flags: X - disabled, A - active, D - dynamic,
C - connect, S - static, r - rip, b - bgp, o - ospf
# DST-ADDRESS G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE
0 A S 10.1.12.0/24 r 192.168.0.253 Local
1 ADC 10.5.8.0/24 Public
2 ADC 192.168.0.0/24 Local
3 A S 0.0.0.0/0 r 10.5.8.1 Public
[admin@MikroTik] ip route>
Policy Rules
Submenu level:
/ip route rule Property Description
action (drop | unreachable | lookup; default:
unreachable) - action to be processed on packets matched by this rule:
drop - silently drop packet
unreachable - reply that destination host is unreachable
lookup - lookup route in given routing table
dst-address (
IP address mask) - destination IP address/mask
interface (
name; default:
"") - interface through which the gateway can be reached
routing-mark (
name; default:
"") - mark of the packet to be mached by this rule. To add a routing mark, use '/ip firewall mangle' commands
src-address (
IP address mask) - source IP address/mask
table (
name; default:
"") - routing table, created by user
Notes
You can use policy routing even if you use masquerading on your private networks. The source address will be the same as it is in the local network. In previous versions of RouterOS the source address changed to 0.0.0.0
It is impossible to recognize peer-to-peer traffic from the first packet. Only already established connections can be matched. That also means that in case source NAT is treating Peer-to-Peer traffic differently from the regular traffic, Peer-to-Peer programs will not work (general application is policy-routing redirecting regular traffic through one interface and Peer-to-Peer traffic - through another). A known workaround for this problem is to solve it from the other side: making not Peer-to-Peer traffic to go through another gateway, but all other useful traffic go through another gateway. In other words, to specify what protocols (HTTP, DNS, POP3, etc.) will go through the gateway A, leaving all the rest (so Peer-to-Peer traffic also) to use the gateway B (it is not important, which gateway is which; it is only important to keep Peer-to-Peer together with all traffic except the specified protocols)
Example
To add the rule specifying that all the packets from the 10.0.0.144 host should lookup the mt routing table:
[admin@MikroTik] ip firewall mangle add action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=mt \
\... chain=prerouting
[admin@MikroTik] ip route> add gateway=10.0.0.254 routing-mark=mt
[admin@MikroTik] ip route rule> add src-address=10.0.0.144/32 \
\... table=mt action=lookup
[admin@MikroTik] ip route rule> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid
0 src-address= 192.168.0.144/32 action=lookup table=mt
[admin@MikroTik] ip route rule>
Application Examples
Static Equal Cost Multi-Path routing
Consider the following situation where we have to route packets from the network 192.168.0.0/24 to 2 gateways - 10.1.0.1 and 10.1.1.1:

Note that the ISP1 gives us 2Mbps and ISP2 - 4Mbps so we want a traffic ratio 1:2 (1/3 of the source/destination IP pairs from 192.168.0.0/24 goes through ISP1, and 2/3 through ISP2).
IP addresses of the router:
[admin@ECMP-Router] ip address> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 Local
1 10.1.0.2/28 10.1.0.0 10.1.0.15 Public1
2 10.1.1.2/28 10.1.1.0 10.1.1.15 Public2
[admin@ECMP-Router] ip address>
Add the default routes - one for ISP1 and 2 for ISP2 so we can get the ratio 1:3:
[admin@ECMP-Router] ip route> add gateway=10.1.0.1,10.1.1.1,10.1.1.1
[admin@ECMP-Router] ip route> print
Flags: X - disabled, A - active, D - dynamic,
C - connect, S - static, r - rip, b - bgp, o - ospf
# DST-ADDRESS G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE
0 ADC 10.1.0.0/28 Public1
1 ADC 10.1.1.0/28 Public2
2 ADC 192.168.0.0/24 Local
3 A S 0.0.0.0/0 r 10.1.0.1 Public1
r 10.1.1.1 Public2
r 10.1.1.1 Public2
[admin@ECMP-Router] ip route>
Standard Policy-Based Routing with Failover
This example will show how to route packets, using an administrator defined policy. The policy for this setup is the following: route packets from the network 192.168.0.0/24, using gateway 10.0.0.1, and packets from network 192.168.1.0/24, using gateway 10.0.0.2. If GW_1 does not respond to pings, use GW_Backup for network 192.168.0.0/24, if GW_2 does not respond to pings, use GW_Backup also for network 192.168.1.0/24 instead of GW_2.
The setup:
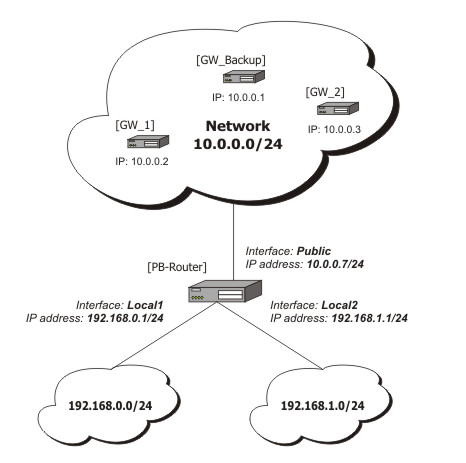
Configuration of the IP addresses:
[admin@PB-Router] ip address> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 192.168.0.1/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 Local1
1 192.168.1.1/24 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.255 Local2
2 10.0.0.7/24 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.255 Public
[admin@PB-Router] ip address>
To achieve the described result, follow these configuration steps:
-
Mark packets from network 192.168.0.0/24 with a new-routing-mark=net1, and packets from network 192.168.1.0/24 with a new-routing-mark=net2 :
[admin@PB-Router] ip firewall mangle> add src-address=192.168.0.0/24 \
\... action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=net1 chain=prerouting
[admin@PB-Router] ip firewall mangle> add src-address= 192.168.1.0/24 \
\... action=mark-routing new-routing-mark=net2 chain=prerouting
[admin@PB-Router] ip firewall mangle> print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
0 chain=prerouting src-address=192.168.0.0/24 action=mark-routing
new-routing-mark=net1
1 chain=prerouting src-address=192.168.1.0/24 action=mark-routing
new-routing-mark=net2
[admin@PB-Router] ip firewall mangle>
-
Route packets from network 192.168.0.0/24 to gateway GW_1 (10.0.0.2), packets from network 192.168.1.0/24 to gateway GW_2 (10.0.0.3), using the according packet marks. If GW_1 or GW_2 fails (does not reply to pings), route the respective packets to GW_Main (10.0.0.1):
[admin@PB-Router] ip route> add gateway=10.0.0.2 routing-mark=net1 \
\... check-gateway=ping
[admin@PB-Router] ip route> add gateway=10.0.0.3 routing-mark=net2 \
\... check-gateway=ping
[admin@PB-Router] ip route> add gateway=10.0.0.1
[admin@PB-Router] ip route> print
Flags: X - disabled, A - active, D - dynamic,
C - connect, S - static, r - rip, b - bgp, o - ospf
# DST-ADDRESS PREFSRC G GATEWAY DISTANCE INTERFACE
0 ADC 10.0.0.0/24 10.0.0.7 Public
1 ADC 192.168.0.0/24 192.168.0.1 Local1
2 ADC 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.1.1 Local2
3 A S 0.0.0.0/0 r 10.0.0.2 Public
4 A S 0.0.0.0/0 r 10.0.0.3 Public
5 A S 0.0.0.0/0 r 10.0.0.1 Pub